In a Nutshell (🌰)
- SSH is the primary secure connection method for managing devices in SSM
- Three authentication methods available: password, SSH key, and passwordless
- Credentials are securely encrypted using Ansible Vault (AES-256)
- Properly configured SSH enables terminal access, container management, and automation
- Advanced settings allow customization for specific network environments
Overview
Secure Shell (SSH) is the foundation of SSM's agentless architecture, providing secure remote access to your devices without requiring additional software installation. This guide covers all SSH configuration options within the SSM interface.
SSH Configuration Interface
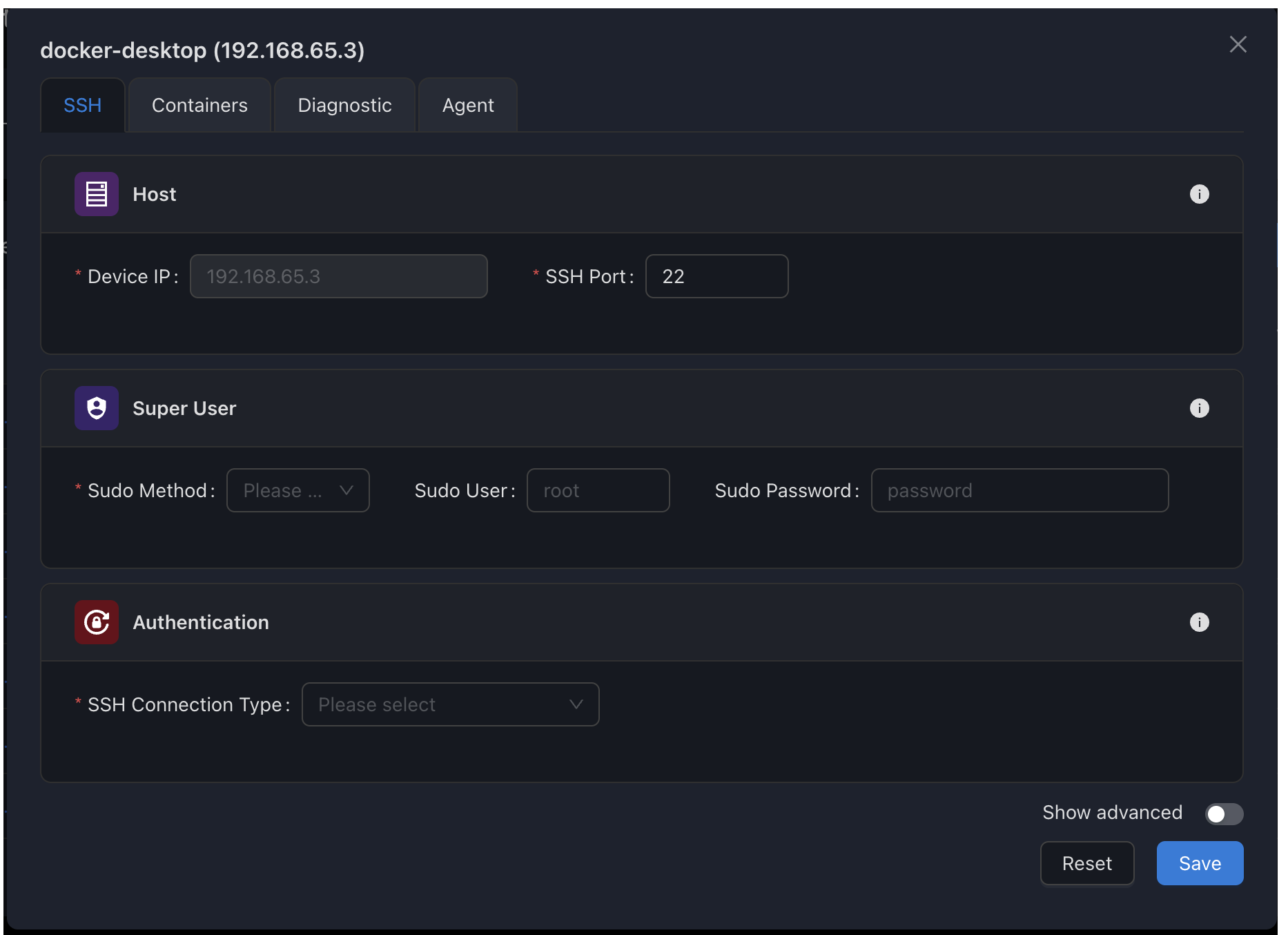
The SSH configuration tab in the device settings provides all options needed to establish a secure connection to your device.
Access Device Configuration
From the Devices page, click on the ⚙️ Configuration button for your device.
Navigate to SSH Tab
Select the SSH tab in the configuration panel (this is the default tab).
Configure Connection Settings
Enter host information, authentication details, and optional advanced settings.
Test Connection
Use the Diagnostic tab to verify your connection settings before saving.
Host Configuration
The Host section defines the basic connection parameters needed to reach your device on the network.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Device IP | ⚠️ | The IPv4 address or hostname of the device. Must be reachable from the SSM instance. |
| SSH Port | ⚠️ | The SSH port number for the device. Default is 22, but can be customized for security. |
Important
Ensure your network configuration allows SSH traffic between the SSM server and your device. This may require firewall configuration on both ends.
Super User Configuration
The Super User section defines how SSM gains elevated privileges on the remote device when needed for operations like Docker management or system configuration.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sudo Method | ⚠️ | The command used for privilege escalation. Almost always sudo on Linux systems. |
| Sudo User | ⭕ | The username to switch to when elevation is needed. Optional if the main user has sudo access. |
| Sudo Password | ⭕ | The password for the sudo user, if required. Many systems are configured for passwordless sudo. |
TIP
If your system uses passwordless sudo (common for many Linux distributions), you can leave the Sudo Password field empty.
Authentication Methods
SSM supports three methods for authenticating with your devices. Choose the most appropriate option based on your security requirements and environment.
Password Authentication
Simple username and password authentication. Quick to set up but less secure for production environments.
SSH Key Authentication
Public/private key authentication. The most secure option and recommended for production use.
Passwordless Authentication
Uses existing SSH agent or host-based authentication. Convenient for development environments.
1. Password Authentication
Password authentication is the simplest method, requiring just a username and password.
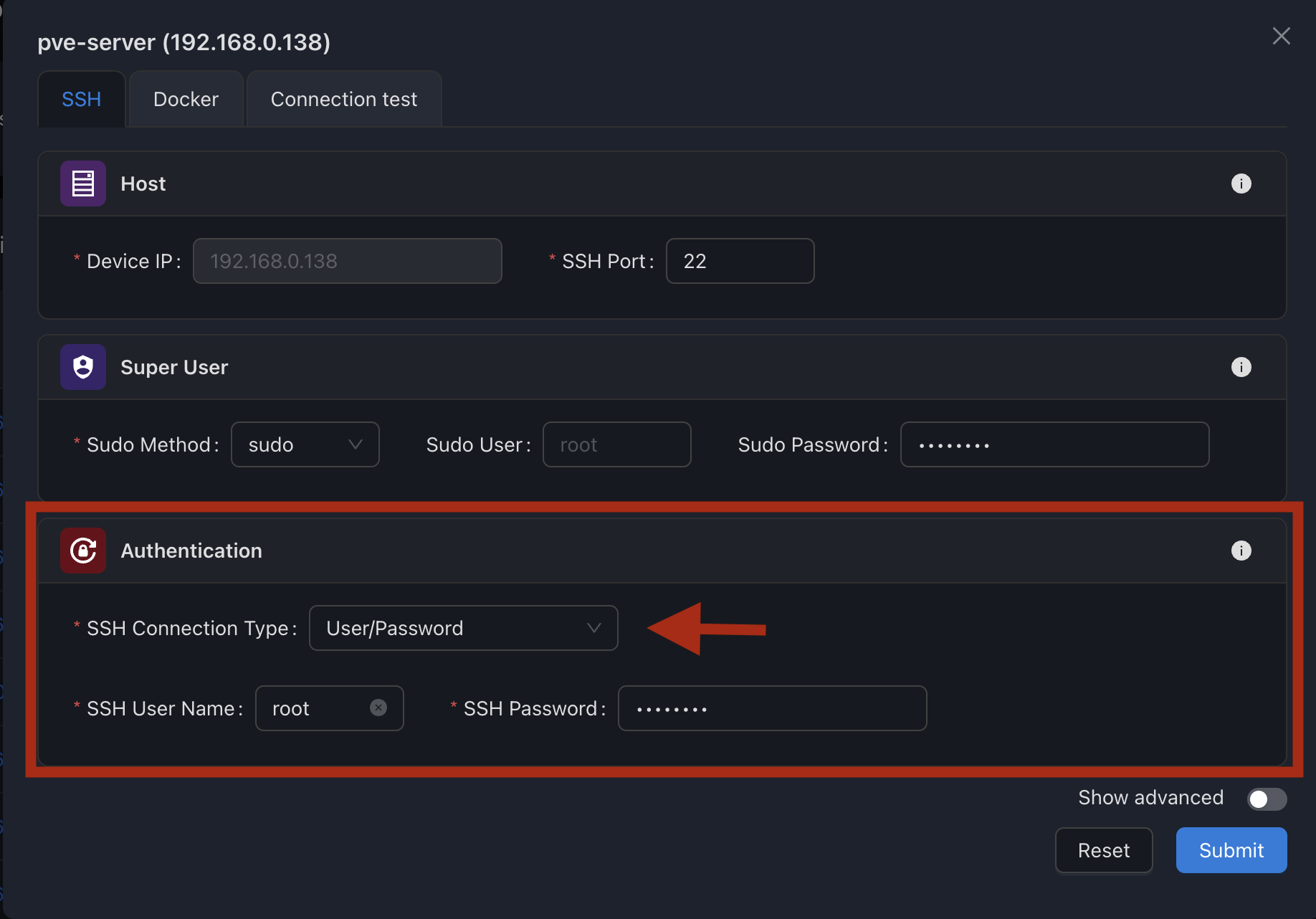
Configuration Steps:
- Select User/Password as the SSH Connection Type
- Enter the Username for the SSH account
- Enter the Password for the SSH account
Security Note
Password authentication is more vulnerable to brute force attacks. Consider using key-based authentication for production environments.
2. SSH Key Authentication
SSH key authentication is more secure and uses a cryptographic key pair instead of a password.
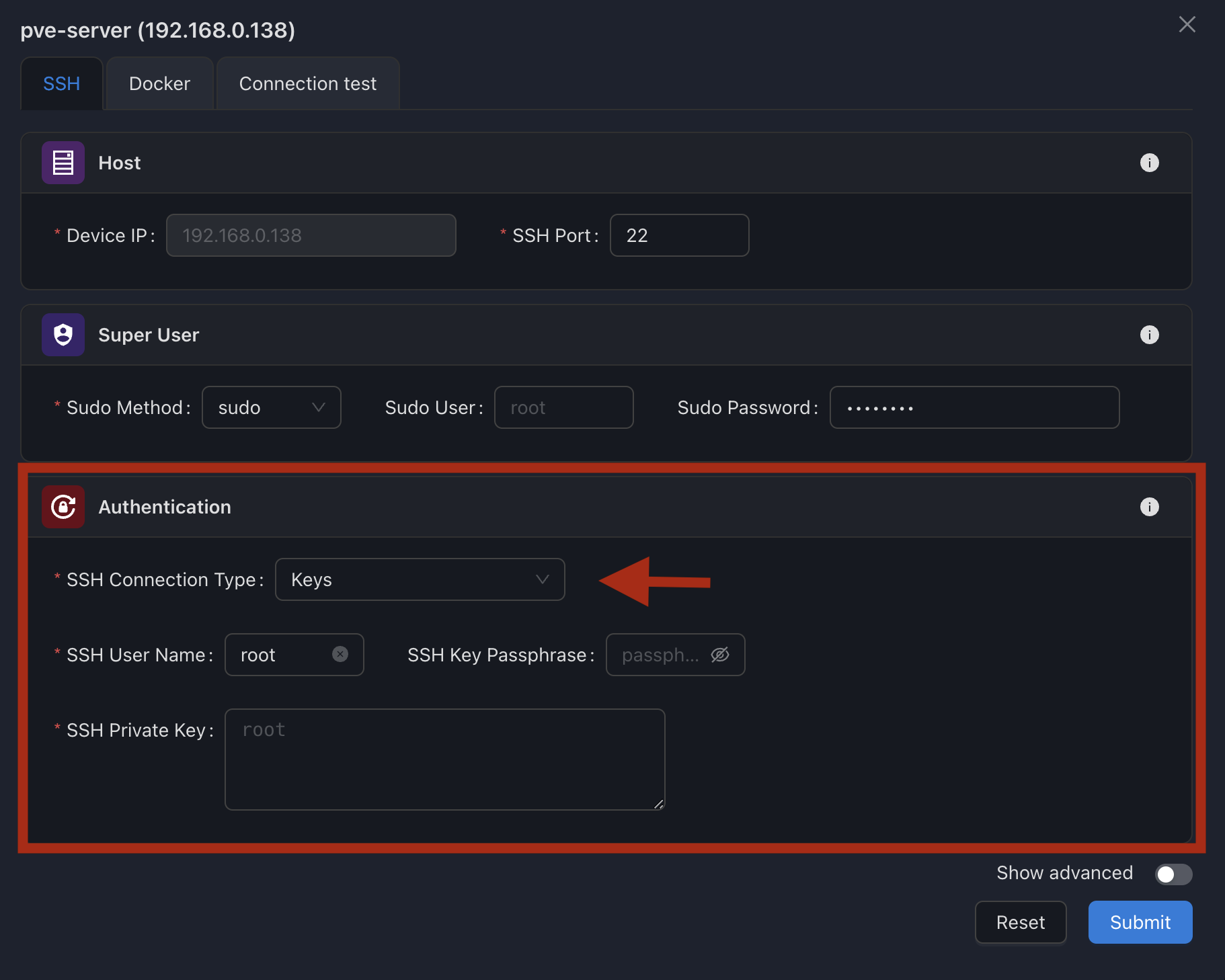
Configuration Steps:
- Select Keys as the SSH Connection Type
- Enter the Username for the SSH account
- Paste your Private Key in PEM format
- Optionally enter a Passphrase if your key is protected
Linux
Generate an SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"Copy public key to your device:
ssh-copy-id username@device-ipWindows
Generate an SSH key pair (PowerShell):
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"Copy public key to your device (manually or using SSH tools)
3. Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication relies on your system's SSH agent or host-based authentication and requires no credentials to be stored in SSM.
Configuration Steps:
- Select Passwordless as the SSH Connection Type
- Enter the Username for the SSH account
TIP
This method requires that your SSH environment is already configured with the appropriate trust relationships between the SSM server and your device.
Advanced Settings
For non-standard environments or specific requirements, SSM provides advanced SSH configuration options.
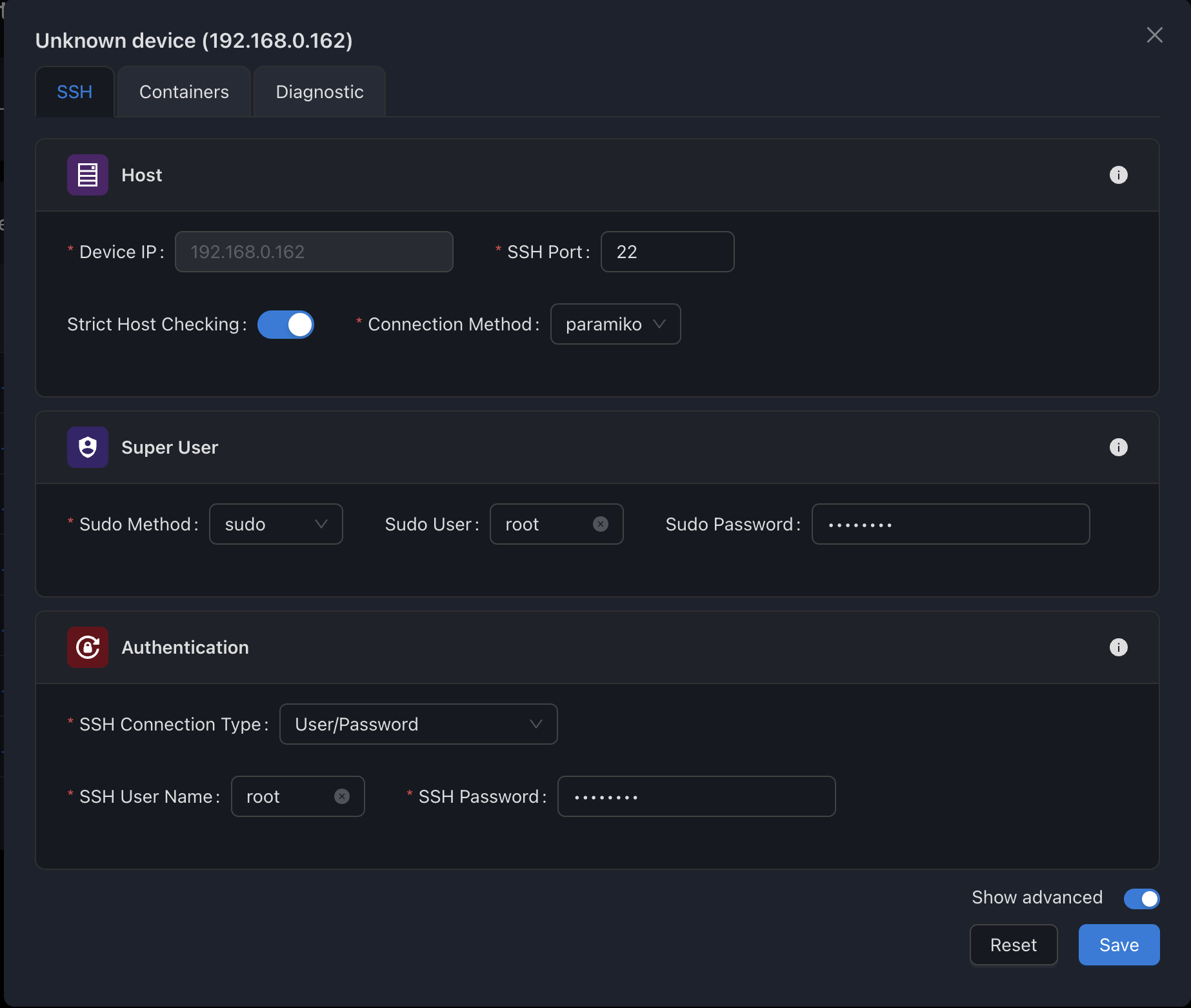
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Force IPv4/IPv6 | Force a specific IP protocol version | Disabled |
| Ansible Connection | Custom connection method | 'smart' |
| Ansible Port | Custom port for Ansible connections | Same as SSH port |
| Ansible Become | Advanced privilege escalation | Disabled |
| Ansible Become Method | Method for privilege escalation | 'sudo' |
TIP
Most users do not need to modify the advanced settings. These options are primarily for specialized environments or troubleshooting specific issues.
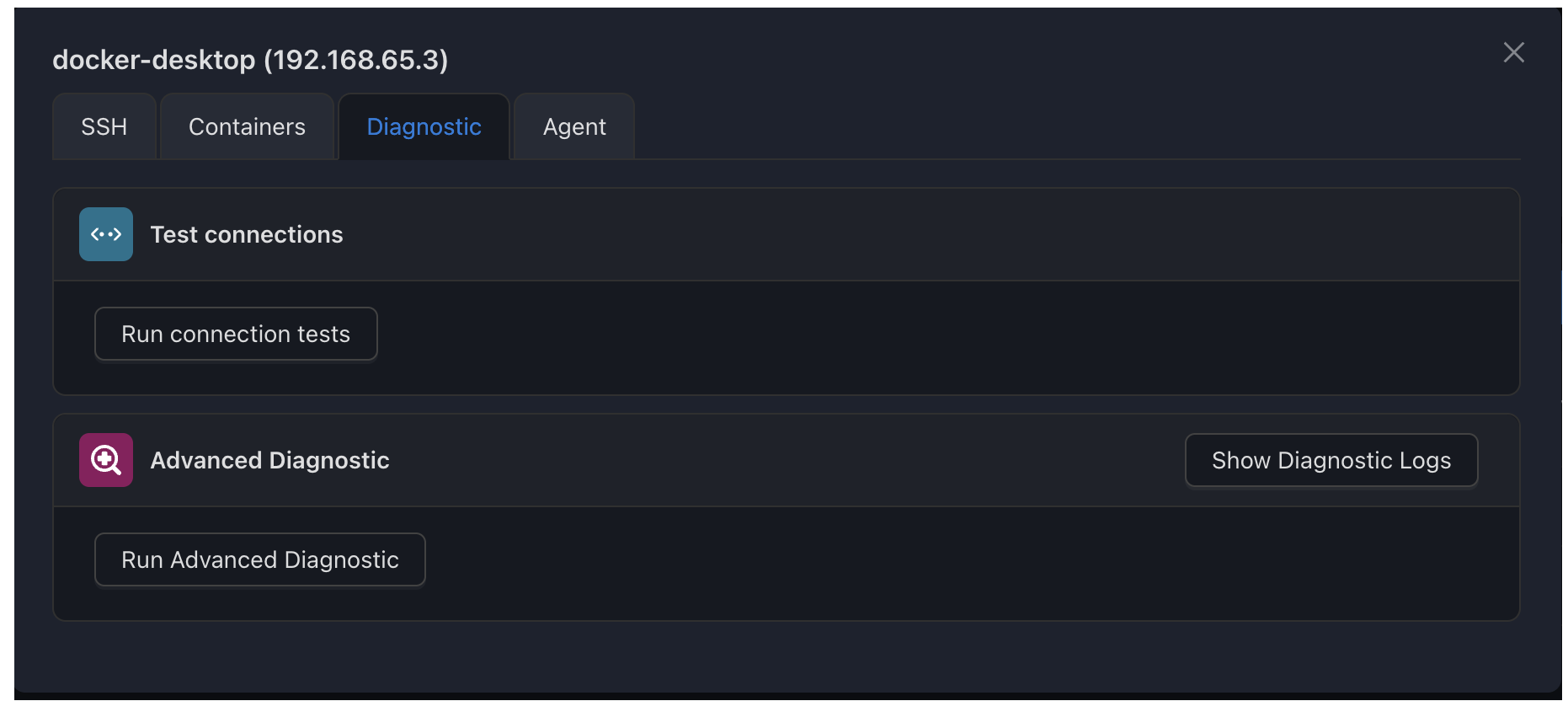
Testing Your Connection
After configuring SSH settings, you should always test the connection before saving.
Go to Diagnostic Tab
Switch to the Diagnostic tab in the device configuration panel.
Run Basic Test
Click Basic Test to verify basic SSH connectivity.
Run Advanced Test
For more detailed diagnostics, click Advanced Test.
Review Results
Check the test results and fix any issues before saving.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues with your SSH configuration, try these common solutions:
| Problem | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Connection Refused | • Verify SSH service is running on the device • Check firewall settings on both SSM server and device • Verify the SSH port configuration |
| Authentication Failed | • Double-check username and password • Verify SSH key format and permissions • Ensure the user has SSH access on the device |
| Permission Denied | • Verify sudo permissions for the user • Check if the user is in required groups (docker, sudo) • Ensure proper file permissions for SSH keys |
| Connection Timeout | • Verify network connectivity between SSM and the device • Check for network restrictions or VPN issues • Ensure the device IP is correct |
For more comprehensive diagnostic information, see the Diagnostic Tools documentation.
Security Best Practices
To maintain the highest level of security for your SSH connections:
🔐 Use SSH Keys
Prefer SSH key authentication over passwords whenever possible
🔄 Key Rotation
Implement regular key rotation for production environments
👤 Dedicated Users
Create specific users for SSM with appropriate permissions
🛡️ Minimal Privileges
Apply the principle of least privilege to SSH accounts