In a Nutshell (🌰)
- Docker integration lets SSM manage and monitor containers on your remote devices
- SSM uses SSH tunneling to securely connect to Docker without exposing the API
- Configure automatic container watching, statistics collection, and event monitoring
- Set custom polling frequencies to balance real-time data with resource usage
- Advanced options available for TLS, registry authentication, and custom Docker sockets
Overview
Once you add a device to SSM, it automatically discovers and connects to the Docker daemon running on that device. This enables SSM to retrieve containers, images, networks, and volumes while providing real-time monitoring and management capabilities.

The Docker configuration panel allows you to control how SSM connects to and monitors your Docker installations. By default, SSM:
- Connects to the Docker socket via SSH tunneling
- Uses the device's SSH credentials for authentication
- Provides real-time container event monitoring
- Performs periodic container state synchronization
- Collects resource usage statistics

Enable/Disable Docker Capability
The Docker capability toggle controls whether SSM attempts to connect to and manage Docker on the device.
Open Configuration
Access the device configuration panel from the Devices page.
Navigate to Containers Tab
Select the Containers tab in the configuration interface.
Toggle Capability
Enable or disable the Docker capability using the toggle switch.
Save Changes
Apply your configuration changes by clicking Save.
TIP
If your device doesn't have Docker installed or you only want to use SSH functionality, disable this capability to prevent connection attempts and related error messages.
Monitoring Configuration
SSM provides three types of container monitoring that can be individually configured:
👁️ Container Watching
Tracks container existence, states, and metadata with configurable frequency.
📊 Statistics Collection
Monitors resource usage (CPU, memory, network) for running containers.
🔔 Event Monitoring
Listens for real-time container events like starts, stops, and restarts.
Watch Settings
Control which aspects of container monitoring are active:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Watch Containers | ⚠️ | Enable or disable the polling of container information and metadata. This allows SSM to maintain an up-to-date inventory of all containers. |
| Watch Container Stats | ⚠️ | Enable or disable the collection of container resource statistics. This provides CPU, memory, and network usage data. |
| Watch Container Events | ⚠️ | Enable or disable real-time event monitoring. This allows SSM to respond immediately to container state changes. |
Registry Rate Limits
The Watch Containers feature queries container registries to check for available updates.
Public registries like Docker Hub have rate limits.
If you manage many devices, use a longer polling interval to avoid hitting rate limits.
Docker Engine Host Configuration
These settings define how SSM connects to the Docker daemon:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Device IP | ⚠️ | The IPv4 address of the device (read-only, inherited from the SSH configuration). |
| Docker Socket | ⚠️ | The filesystem path to the Docker socket on the remote device. Default is /var/run/docker.sock. |
TIP
Most Docker installations use the default socket path. You only need to modify this setting if your Docker daemon uses a non-standard socket location.
Watcher Crons
Control how frequently SSM polls for container information and statistics:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Watch Containers | ⚠️ | The polling frequency for container inventory updates. Default is hourly (0 * * * *). |
| Watch Container Stats | ⚠️ | The polling frequency for resource usage statistics. Default is every minute (*/1 * * * *). |
Using Cron Expressions
Frequencies are specified using cron expressions, where the fields are: minute hour day-of-month month day-of-week. For example, */5 * * * * means every 5 minutes.
Balancing Frequency and Load
Higher polling frequencies provide more accurate data but increase network traffic and server load. Choose a frequency that meets your monitoring needs without overloading your systems.
Advanced Configuration
For specialized environments or enhanced security, SSM provides advanced Docker configuration options.
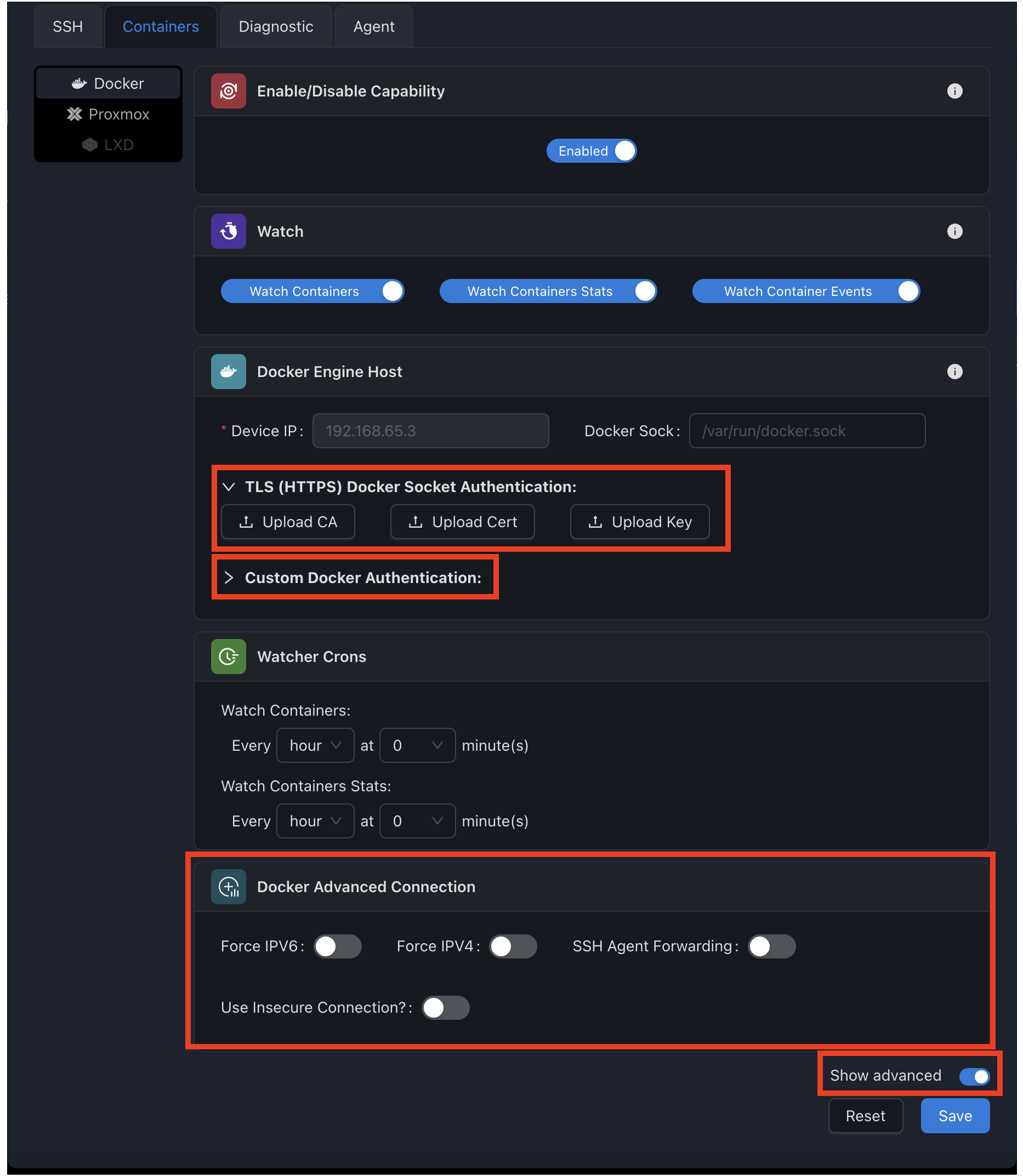
Access these options by clicking the "Show Advanced" toggle at the bottom of the configuration panel.
Alternative Authentication Methods
By default, SSM uses the device's SSH configuration to connect to Docker. The advanced options allow you to:
- Use custom SSH credentials for Docker access
- Configure TLS for direct Docker API connections
- Set additional connection parameters
TLS Secure Connection
For environments where Docker is exposed over TCP with TLS encryption:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| CA Certificate | The Certificate Authority certificate used to verify the Docker server. |
| Client Certificate | The client certificate for mutual TLS authentication. |
| Client Key | The private key associated with the client certificate. |
Security Note
Direct connections to the Docker API (even with TLS) should only be used in secure environments. SSH tunneling is the preferred method for production deployments.
Container Update Detection
SSM automatically checks for container image updates based on:
- Semantic Version Tags: For images following version numbering (e.g., 1.2.3)
- Image Digests: For images using floating tags like "latest"

You can customize update detection using Docker labels:
services:
myapp:
image: myorg/myapp:latest
labels:
ssm.watch: "true" # Control if container is watched
ssm.watch.tag.include: "v*,stable" # Include only specific tags
ssm.watch.tag.exclude: "*-beta" # Exclude certain tagsTroubleshooting
If you encounter issues with Docker integration, try these common solutions:
| Issue | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Connection Failed | • Verify Docker is running on the device • Check that the SSH user has access to the Docker socket • Verify the Docker socket path ( /var/run/docker.sock by default) |
| Permission Denied | • Add the SSH user to the docker group: sudo usermod -aG docker $USER• Set permissions on the Docker socket: sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock |
| Updates Not Detected | • Check registry authentication for private images • Verify image uses semantic versioning for tag-based updates • Enable digest watching for floating tags like "latest" |
| High Resource Usage | • Reduce polling frequency in the Watcher Crons settings • Disable statistics collection for non-critical containers |
For more comprehensive diagnosis, use the Diagnostic Tools to test your Docker connection.
Best Practices
🔐 Security First
Use SSH tunneling instead of direct TCP connections when possible.
👤 Dedicated Users
Create a dedicated user for Docker management with appropriate permissions.
⚖️ Optimize Polling
Balance monitoring frequency with resource usage and registry rate limits.
🏷️ Container Labels
Use SSM labels to control monitoring behavior for individual containers.