Ansible Connection
Supported Methods
SSM currently supports two connection methods:
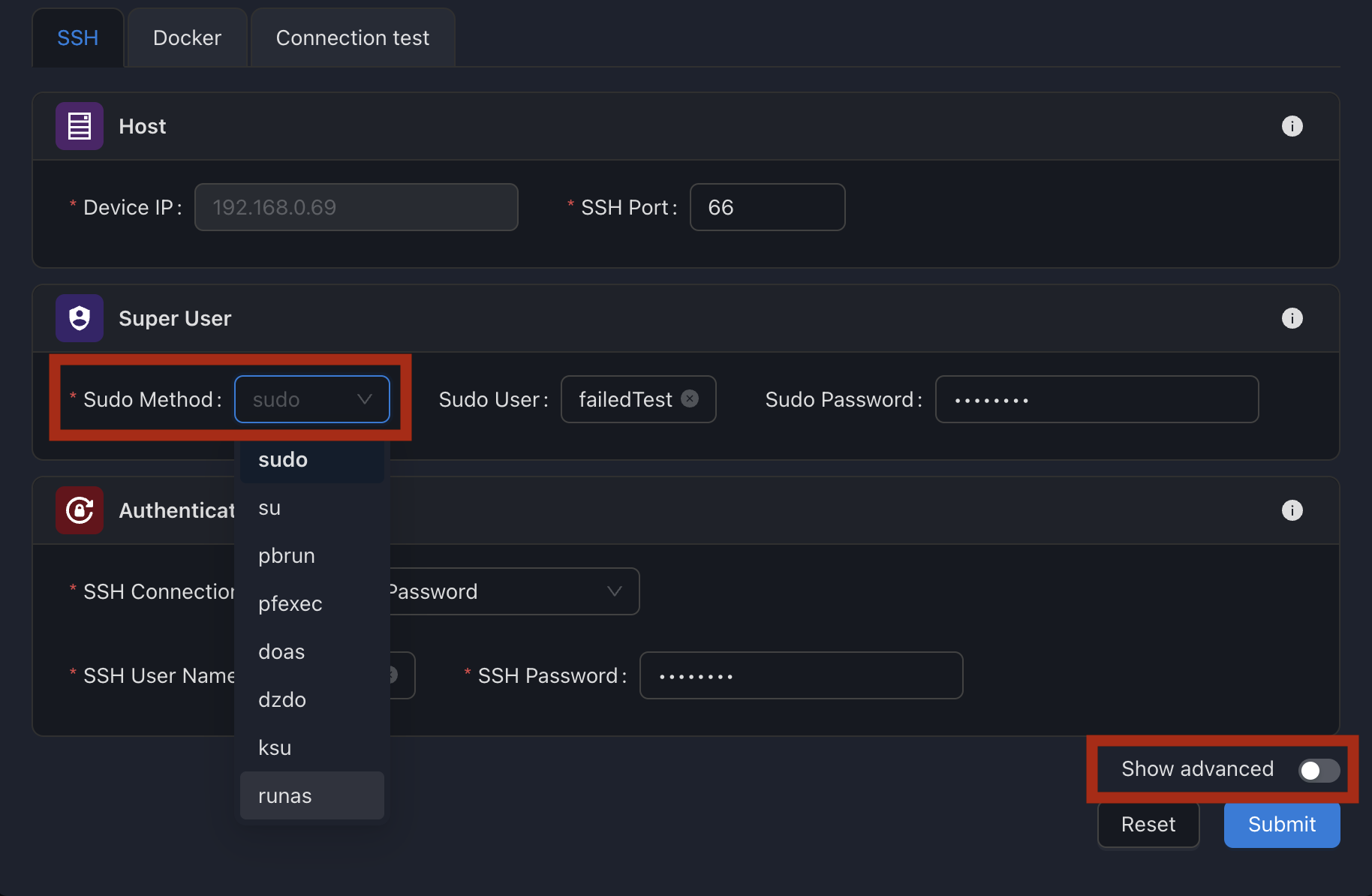
Paramiko(default)SSH (OpenSSH)
By default, SSM uses Paramiko to support various underlying connection configurations (passwords, key, key + passphrase).
If you experience connection issues, try using the SSH (OpenSSH) option in the Configuration modal of your device in the Inventory (Show advanced must be on).
| Feature | Classic SSH (OpenSSH) | Paramiko (default) |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Native SSH client (OpenSSH) | Pure Python library |
| Performance | Generally faster | Typically slower due to Python |
| Compatibility | Widely available on Unix-like systems | Useful where OpenSSH is not available |
| Security | High, relies on OpenSSH security practices | Secure, but Python implementation may lag behind OpenSSH updates |
| Fallback/Alternative | Default method | Alternative method |
| Dependencies | Requires OpenSSH | Pure Python, no extra native dependencies |
| Features | Full OpenSSH feature support | Limited compared to OpenSSH |
| Use Case | Standard and preferred for most environments | Specific scenarios where OpenSSH is not feasible |
Limitations of SSH (OpenSSH)
The SSH (OpenSSH) does NOT support using an SSH key with a passphrase.
Changing the connection method
Inventory/<device>/Configuration => "SSH" tab ; Show advanced on;
Ansible Become (aka sudo)
The become method in Ansible is used to escalate privileges and run tasks with higher permissions than that of the current user. This is particularly useful for performing administrative tasks that require superuser or other privilege elevation on remote machines.
become allows users to achieve this escalation in a controlled and secure manner, using mechanisms like sudo, su, pbrun, and others.
The configuration for the sudo user credentials must be specified in the Device configuration.
Become
To install the SSM agent, configuring a become method is mandatory.
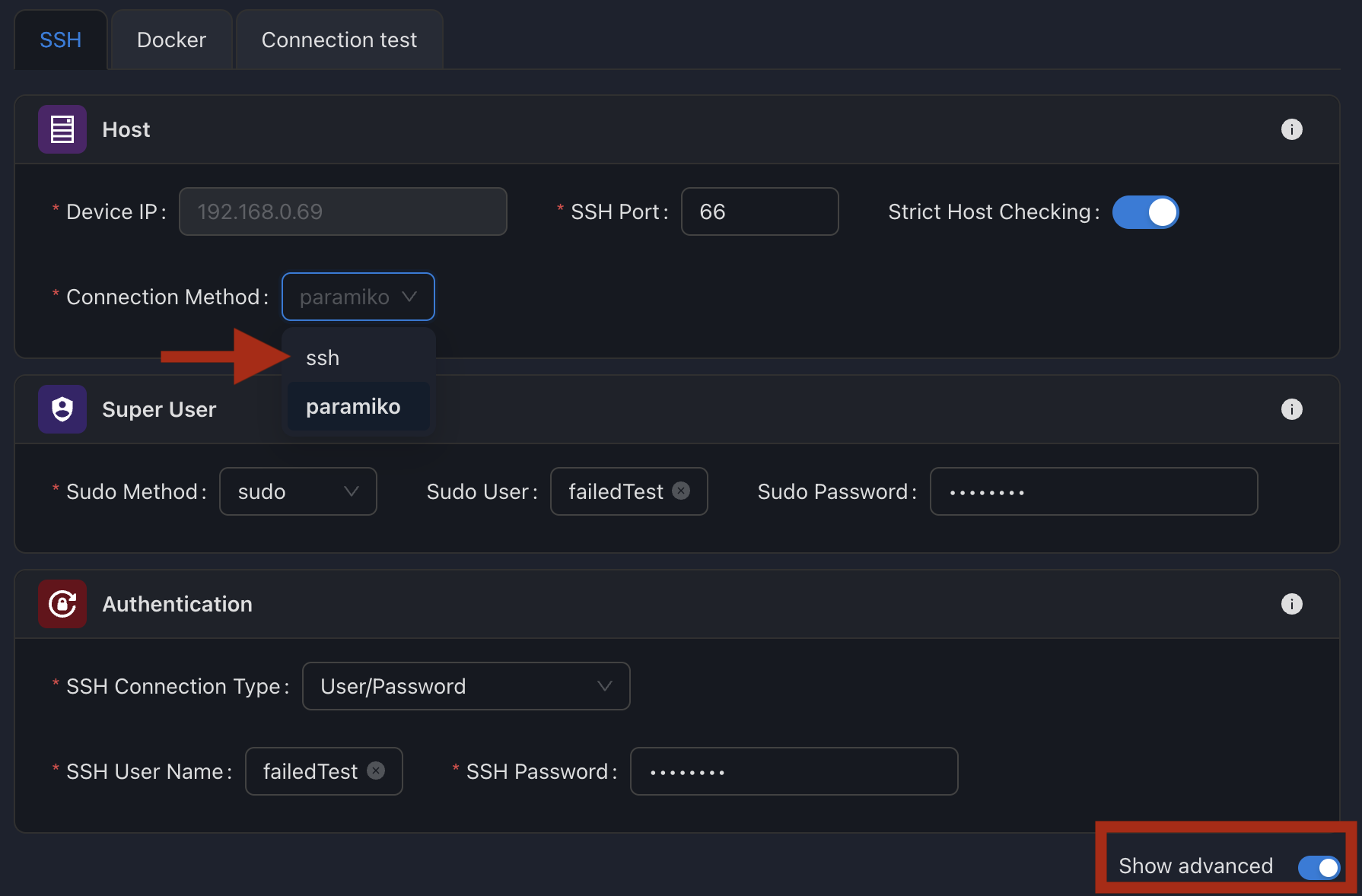
SSM supports the following methods:
sudo(default): Default method, commonly used to run commands as the superuser or another user with sudo privileges.su: Switches user to execute tasks with the privileges of another user.pbrun: A method used in environments wherepbrunis available, often in certain enterprise systems.pfexec: Primarily used on Solaris systems.doas: Relevant for OpenBSD systems.ksu: Used with Kerberos-based systems.dzdo: Used in environments where Centrify's Direct Authorize is available.
Changing the connection method
Inventory/<device>/Configuration => "SSH" tab ; Show advanced on;